
2.)Analysis of the various waves and normal vectors of depolarization and repolarization yields important diagnostic information.


ADVANTAGES
1.)It is the gold standard for the diagnosis of cardiac arrhythmias.


2.)It guides therapy and risk stratification for patients with suspected acute myocardial infarction.
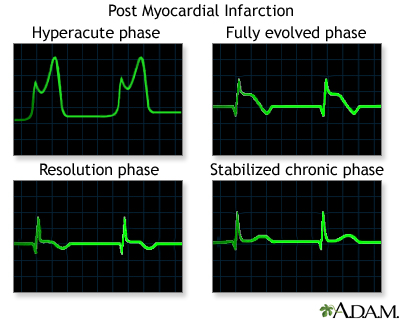
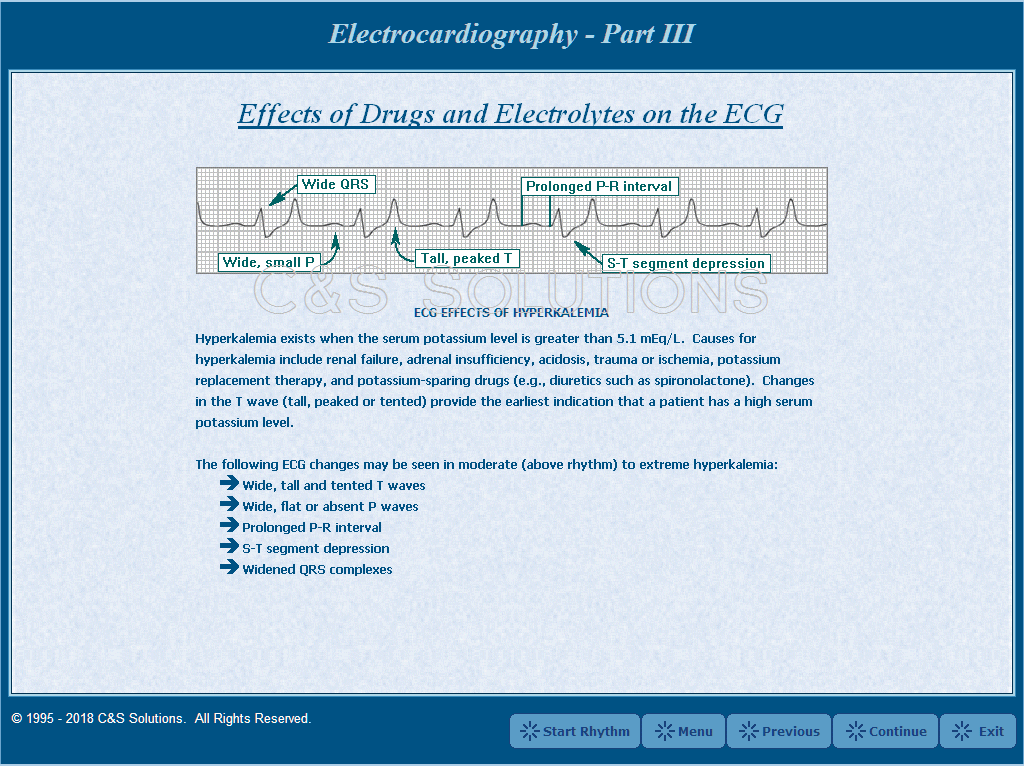
3.)It helps detect electrolyte disturbances (e.g. hyperkalemia and hypokalemia).

4.)It allows for the detection of conduction abnormalities (e.g. right and left bundle branch block).


5.)It is used as a screening tool for ischemic heart disease during a cardiac stress test.

6.)It is occasionally helpful with non-cardiac diseases (e.g. pulmonary embolism or hypothermia).


7.)The electrocardiogram does not directly assess the contractility of the heart. However, it can give a rough indication of increased or decreased contractility.




wonderful illustrations...tks...
ReplyDelete