Implied by this definition is the fact that the device must not need to be continuously tethered to a stationary power supply, or other stationary resources, such as filters or chemical processing units. (Periodic rapid recharging of batteries, refilling of chemicals, and/or cleaning/replacing of filters, would not exclude a device from being called an artificial organ.) Thus a dialysis machine, while a very successful and critically important life support device that completely replaces the duties of a kidney, is not an artificial organ. At this time a successful portable self-contained artificial kidney has not become available.
Reasons to construct and install an artificial organ, an extremely expensive process initially, which may entail many years of ongoing maintenance services not needed by a natural organ, might include:
1.) Life support to prevent imminent death while awaiting a transplant (e.g. artificial heart)

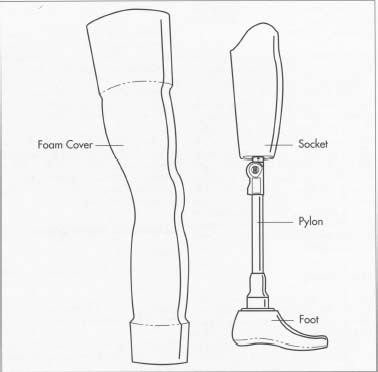
2.)Dramatic improvement of the patient's ability for self care (e.g. artificial limb)
3.)Improvement of the patient's ability to interact socially (e.g. cochlear implant)

4.)Cosmetic restoration after cancer surgery or accident

The use of any artificial organ by humans is almost always preceded by extensive experiments with animals. Initial testing in humans is frequently limited to those either already facing death, or who have exhausted every other treatment possibility. (Rarely testing may be done on healthy volunteers who are scheduled for execution pertaining to violent crimes.)
Although not typically thought of as organs, one might also consider replacement bone, and joints thereof, such as hip replacements, in this context.

ARTIFICIAL CARDIA
The name might imply the heart, but this pertains to gastric repairs, specifically of the valves at either end of the stomach.

ARTIFICIAL EYE
The most successful function-replacing artificial eye so far is actually an external miniature digital camera with a remote unidirectional electronic interface implanted on the retina, optic nerve, or other related locations inside the brain. The present state of the art yields only very partial functionality, such as recognizing levels of brightness, swatches of color, and/or basic geometric shapes, proving the concept's potential. While the living eye is indeed a camera, it is also much more than that.

Various researchers have demonstrated that the retina performs strategic image preprocessing for the brain. The problem of creating a 100% functional artificial electronic eye is even more complex than what is already obvious. Steadily increasing complexity of the artificial connection to the retina, optic nerve or related brain areas advances, combined with ongoing advances in computer science, is expected to dramatically improve the performance of this technology.

For the person whose damaged or diseased living eye retains some function, other options superior to the electronic eye described above may be available.
None of the current devices presents the cosmetic appearance of a living eye.
ARTIFICIAL HEART
While considered a success, the use of artificial hearts is limited to patients awaiting transplants whose death is imminent. The current state of the art devices are unable to reliably sustain life beyond about 18 months.

ARTIFICIAL PACEMAKERS
These electronic devices, which can either intermittently augment (defibrillator mode), continuously augment, or completely bypass the natural living cardiac pacemaker as needed, are so successful, they have become common place.

ARTIFICIAL ARMS
Artificial arms with semi-functional hands, some even fitted with working opposable "thumbs" plus 2 "fingers", and legs with shock absorbing feet capable of allowing a trained patient to even run, have become available.

ARTIFICIAL URINARY BLADDER
This represents a unique success in that these are autologous laboratory-grown living replacements, as opposed to most other artificial organs which depend upon electro-mechanical contrivances, and may or may not incorporate any living tissue.

ARTIFICIAL PANCREAS
For the treatment of diabetes, numerous promising techniques are currently being tested, including some that incorporate donated living tissue housed in special materials to prevent the patient's immune system from killing the foreign live components.

BRAIN PACEMAKER
These devices, including deep brain stimulators, send electrical impulses to the brain in order to relieve depression, epilepsy, tremors of Parkinson's disease, and other conditions. Rather than replacing existing neural networks to restore function, these devices often serve by disrupting the output of existing malfunctioning nerve centers to eliminate symptoms.

ARTIFICIAL CORPORA CAVERNOSA
To treat erectile disfunction, both corpora cavernosa can be irreversibly surgically replaced with manually inflatable penile implants. This is a drastic therapeutic surgery meant only for men suffering from complete impotence that has resisted all other treatment approaches.

An implanted pump in the groin or scrotum can be manipulated by hand to fill these artificial cylinders, normally sized to be direct replacements for the natural corpus cavernosa, from an implanted reservoir in order to achieve an erection.
RESTORATION
It is also possible to construct and install an artificial organ to give its possessor abilities which are not naturally occurring. While research is proceeding, particularly in areas of vision, memory, and information processing, this idea is presently more in the realm of science fiction than science fact.
Current research focuses on restoring inoperative short-term memory in accident victims and lost access to long-term memory in dementia patients. Success here would lead to widespread interest in applications for persons whose memory is considered healthy to dramatically enhance their memory of far beyond what can be achieved with mnemonic techniques. Given that our understanding of how living memory actually works is incomplete, it is unlikely this scenario will become reality in the near future.
One idea with significant consequences is that of implanting a Language Translator for diplomatic and military applications. While machine translation does exist, it is presently neither good nor small enough to fulfill its promise.
This might also include the existing (and controversial when applied to humans) practice of implanting subcutaneous "chips" (integrated circuits) for identification and location purposes. An example of this is the RFID tags made by VeriChip Corporation.



No comments:
Post a Comment